UNDERSTANDING BASIC COMPUTER TERMS
Data is electronic information.
Type of Hardware | Function | Examples |
Input device | Allows user to enter data and commands | Keyboard, mouse, joystick, microphone |
Output device | Presents processed data to user | Monitor, printer, speaker |
System unit | Processes, stores, and communicates data | CPU, memory chip, hard disk, floppy disk, CD- ROM drive, network card, modem |
INPUT DEVICES
An input device generates input for the computer.
(1) Mouse
A mouse is a small device used to point to and select items on your computer screen. Although mice come in many shapes, the typical mouse does look a bit like an actual mouse. It's small, oblong, and connected to the system unit by a long wire that resembles a tail. Some newer mice are wireless.
A mouse usually has two buttons: A primary button (usually the left button) and a secondary button. Many mice also have a wheel between the two buttons, which allows you to scroll smoothly through screens of information.
When you move the mouse with your hand, a pointer on your screen moves in the same direction. (The pointer's appearance might change depending on where it's positioned on your screen.) When you want to select an item, you point to the item and then click (press and release) the primary button. Pointing and clicking with your mouse is the main way to interact with your computer.
(a) Using your Mouse
Just as you might use your hands to interact with objects in the physical world, you can use your mouse to interact with items on your computer screen. You can move objects, open them, change them, throw them away, and perform other actions, all by pointing and clicking with your mouse.
(i) Basic parts
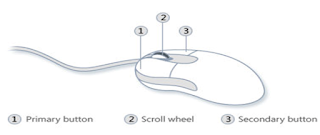
A mouse typically has two buttons: a primary button (usually the left button) and a secondary button (usually the right button). You will use the primary button most often. Most mice also include a scroll wheel between the buttons to help you scroll through documents and webpages more easily. On some mice, the scroll wheel can be pressed to act as a third button. Advanced mice might have additional buttons that can perform other functions.
Parts of a mouse
(ii) Holding and moving the mouse
(iii) Pointing, clicking, and dragging
Pointing to an item on the screen means moving your mouse so the pointer appears to be touching the item. When you point to something, a small box often appears that describes the item. For example, when you point to the Recycle Bin on the desktop, a box appears with this information: "Contains the files and folders that you have deleted."
The pointer can change depending on what you're pointing to. For example, when you point to a link in your web browser, the pointer changes from an arrow
Most mouse actions combine pointing with pressing one of the mouse buttons. There are four basic ways to use your mouse buttons: clicking, double-clicking, right-clicking, and dragging.
(iv) Clicking (single-clicking)
To click an item, point to the item on the screen, and then press and release the primary button (usually the left button).
Clicking is most often used to select (mark) an item or open a menu. This is sometimes called single-clicking or left-clicking.
(v) Double-clicking
To double-click an item, point to the item on the screen, and then click twice quickly. If the two clicks are spaced too far apart, they might be interpreted as two individual clicks rather than as one double-click.
Double-clicking is most often used to open items on your desktop. For example, you can start a program or open a folder by double-clicking its icon on the desktop.
Tips:
· If you have trouble double-clicking, you can adjust the double-click speed (the amount of time acceptable between clicks). Follow these steps:
1. Open Mouse Properties by clicking the Start button
2. Click the Buttons tab, and then, under Double-click speed, move the slider to increase or decrease the speed.
(vi) Right-clicking
To right-click an item, point to the item on the screen, and then press and release the secondary button (usually the right button).
Right-clicking an item usually displays a list of things you can do with the item. For example, when you right-click the Recycle Bin on your desktop, you'll see a menu with options to open it, empty it, delete it, or see its properties. If you're ever unsure of what to do with something, right-click it.
(vii) Dragging
You can move items around your screen by dragging them. To drag an object, point to the object on the screen, press and hold the primary button, move the object to a new location, and then release the primary button.
Dragging (sometimes called dragging and dropping) is most often used to move files and folders to a different location and to move windows and icons around on your screen.
(viii) Using the scroll wheel
If your mouse has a scroll wheel, you can use it to scroll through documents and webpages. To scroll down, roll the wheel backward (toward you). To scroll up, roll the wheel forward (away from you).
(ix) Customizing your mouse
You can change your mouse settings to suit your personal preferences. For example, you can change how fast your mouse pointer moves around the screen, or change the pointer's appearance. If you're left-handed, you can switch the primary button to be the right button.
(x) Tips for using your mouse safely
Holding and moving your mouse properly can help you avoid soreness or injury to your wrists, hands, and arms, particularly if you use your computer for long periods of time. Here are some tips to help you avoid problems:
· Place your mouse at elbow level. Your upper arms should fall relaxed at your sides.
· Don't squeeze or grip your mouse tightly. Hold it lightly.
· Move the mouse by pivoting your arm at your elbow. Avoid bending your wrist up, down, or to the sides.
· Use a light touch when clicking a mouse button.
· Keep your fingers relaxed. Don't allow them to hover above the buttons.
· When you don't need to use the mouse, don't hold it.
· Take short breaks from computer use every 15 to 20 minutes.










Comments
Post a Comment